分布式搜索引擎ElasticSearch教程(作者原创)
个人简介
作者是一个来自河源的大三在校生,以下笔记都是作者自学之路的一些浅薄经验,如有错误请指正,将来会不断的完善笔记,帮助更多的Java爱好者入门。
文章目录
-
- 个人简介
- ElasticSearch7.6.1笔记
-
- ElasticSearch概念
- ElasticSearch的底层索引
- elasticsearch和关系型数据库(MySQL)
- elasticsearch的一些注意点***
-
- 跨域问题
- 占用内存过多导致卡顿问题
- elasticsearch和kibana版本问题
- ik分词器
-
- ik分词器的使用
- ik分词器分词的扩展
- elasticsearch的操作(REST风格)
-
- 创建索引
- 删除索引
- 往索引插入数据(document)
- 删除索引中指定的数据(根据id)
- 修改索引中指定的数据
- 删除索引中指定的数据
- 创建映射字段
-
- 指定索引映射字段只能使用一次***
- 使用"_mapping",往索引添加字段
- 使用_reindex实现数据迁移
- 获取索引信息
- 获取指定索引中所有的记录(_search)
- 获取索引指定的数据
- 获取指定索引全部数据(match_all:{})
- match查询(只允许单个查询条件)
-
- 如果我们再加多一个查询条件
- 精准查询(term)和模糊查询(match)区别
- multi_match实现类似于百度搜索
- 短语(精准)搜索(match_phrase)
- 指定查询显示字段(_source)
- 排序sort
- 分页
- 字段高亮(highlight)
-
- 模仿百度搜索高亮
- bool查询(用作于多条件查询)
- 过滤器,区间条件(filter range)
- 查看整个es的索引信息
- elasticsearch的Java Api
-
- 准备阶段
- 索引操作
-
- 创建索引
- 删除索引
- 检查索引是否存在
- 文档操作
-
- 创建指定id的文档
- 删除指定id的文档
- 修改指定id的文档
- 获取指定id的文档
- 搜索(匹配全文match_all)
- 搜索(模糊查询match)
- 搜索(多字段搜索multi_match)
- 搜索(筛选字段fetchSource)
- 分页、排序、字段高亮
- 布尔搜索(bool)
- es实战(京东商品搜索)
-
- 从京东上爬取数据
ElasticSearch7.6.1笔记
ElasticSearch概念
elasticsearch是一个实时的分布式全文检索引擎,elasticsearch是由Lucene作为底层构建的,elasticsearch采用的不是一般的正排索引(类似于mysql索引),而是用倒排索引,好处是模糊搜索速度极快。。。
elasticsearch的操作都是使用JSON格式发送请求的
ElasticSearch的底层索引
我们知道mysql的like可以作为模糊搜索,但是速度是很慢的,因为mysql的like模糊搜索不走索引,因为底层是正排索引,所谓的正排索引,也就是利用完整的关键字去搜索。。。。而elasticsearch的倒排索引则就是利用不完整的关键字去搜索。原因是elasticsearch利用了“分词器”去对每个document分词(每个字段都建立了一个倒排索引,除了documentid),利用分出来的每个词去匹配各个document
比如:在索引名为hello下,有三个document
documentid age name
1 18 张三
2 20 李四
3 18 李四
此时建立倒排索引:
第一个倒排索引:
age
18 1 , 3
20 2
第二个倒排索引:
name
张三 1
李四 2 , 3
elasticsearch和关系型数据库(MySQL)
我们暂且可以把es和mysql作出如下比较
mysql数据库(database) ========== elasticsearch的索引(index)
mysql的表(table)==============elasticsearch的type(类型)======后面会被废除
mysql的记录 =========== elasticsearch的文档(document)
mysql的字段 ============= elasticsearch的字段(Field)
elasticsearch的一些注意点***
跨域问题
打开elasticsearch的config配置文件elasticsearch.yml
并在最下面添加如下:
http.cors.enabled: truehttp.cors.allow-origin: "*"占用内存过多导致卡顿问题
因为elasticsearch是一个非常耗资源的,从elasticsearch的配置jvm配置文件就可以看到,elasticsearch默认启动就需要分配给jvm1个g的内存。我们可以对它进行修改
打开elasticsearch的jvm配置文件jvm.options
找到:
-Xms1g //最小内存-Xms1g //最大内存修改成如下即可:
-Xms256m-Xms512melasticsearch和kibana版本问题
如果在启动就报错,或者其他原因,我们要去看一看es和kibana的版本是否一致,比如es用的是7.6 ,那么kibana也要是7.6
ik分词器
ik分词器的使用
ik分词器是一种中文分词器,但是比如有一些词(例如人名)它是不会分词的,所以我们可以对它进行扩展。
要使用ik分词器,就必须下载ik分词器插件,放到elasticsearch的插件目录中,并以ik为目录名
ik分词器一共有两种分词方式:ik_smart , ik_max_word
ik_smart : 最少切分(尽可能少切分单词)
ik_max_word : 最多切分 (尽可能多切分单词)
=============================
ik_smart :
GET _analyze // _analyze 固定写法{ "text": ["分布式搜索"], "analyzer": "ik_smart" }ik_max_word :
GET _analyze{ "text": ["分布式搜索"], "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }ik分词器分词的扩展
GET _analyze{ "text": ["我是张三,very nice"], "analyzer": "ik_max_word"}人名没有分正确。我们可以新建一个配置文件,去添加我们需要分的词
1.我们先去ik插件目录中找到IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml文件
<properties><comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment><entry key="ext_dict"></entry> //如果有自己新建的dic扩展,就可以加到<entry>xxx.dic</entry> <entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry><!-- words_location --><!-- words_location --></properties>2.创建my.dic,把自己需要分词的添加进去
比如我们想添加多“张三”这个分词,就可以在my.dic输入进去
3.重启所有服务即可
GET _analyze{ "text": ["我是张三,very nice"], "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }{ "tokens" : [ { "token" : "我", "start_offset" : 0, "end_offset" : 1, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 0 }, { "token" : "是", "start_offset" : 1, "end_offset" : 2, "type" : "CN_CHAR", "position" : 1 }, { "token" : "张三", "start_offset" : 2, "end_offset" : 5, "type" : "CN_WORD", "position" : 2 }, { "token" : "very", "start_offset" : 6, "end_offset" : 10, "type" : "ENGLISH", "position" : 3 }, { "token" : "nice", "start_offset" : 11, "end_offset" : 15, "type" : "ENGLISH", "position" : 4 } ]}elasticsearch的操作(REST风格)
下面的操作使用Kibana作为可视化工具去操作es ,也可以使用postman去操作
method url地址 描述
PUT localhost:9100/索引名称/类型名称/文档id 创建文档(指定id)
POST localhost:9100/索引名称/类型名称 创建文档(随机id)
POST localhost:9100/索引名称/文档类型/文档id/_update 修改文档
DELETE localhost:9100/索引名称/文档类型/文档id 删除文档
GET localhost:9100/索引名称/文档类型/文档id 查询文档通过文档id
POST localhost:9100/索引名称/文档类型/_search 查询所有文档
可以看到,elasticsearch和原生的RESTful风格有点不同,区别是PUT和POST,原生RestFul风格的PUT是用来修改数据的,POST是用来添加数据的,而这里相反
PUT和POST的区别:
PUT具有幂等性,POST不具有幂等性,也就是说利用PUT无论提交多少次,返回结果都不会发生改变,这就是具有幂等性,而POST我们可以把他理解为uuid生成id,每一次的id都不同,所以POST不具有幂等性
创建索引
模板:PUT /索引名
例1:
创建一个索引名为hello01,类型为_doc,documentid(记录id)为001的记录,PUT一定要指定一个documentid,如果是POST的话可以不写,POST是随机给documentid的,因为post是不具有幂等性的
PUT /hello03{ //请求体,为空就是没有任何数据}返回结果
{ "acknowledged" : true, "shards_acknowledged" : true, "index" : "hello03"}删除索引
DELETE hello01{ }往索引插入数据(document)
PUT /hello03/_doc/1{ "name": "yzj", "age" : 18 }结果:
{ "_index" : "hello03", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_version" : 1, "result" : "created", "_shards" : { "total" : 2, "successful" : 1, "failed" : 0 }, "_seq_no" : 0, "_primary_term" : 1}然后我们查看一下hello03的索引信息:
{"state": "open","settings": {"index": {"creation_date": "1618408917052","number_of_shards": "1","number_of_replicas": "1","uuid": "OEVNL7cCQgG74KMPG5LjLA","version": {"created": "7060199"},"provided_name": "hello03"}},"mappings": {"_doc": {"properties": {"name": {"type": "text","fields": {"keyword": {"ignore_above": 256,"type": "keyword" //name的底层默认用了keyword(不可分词)}}},"age": {"type": "long" //age用了long}}}},"aliases": [ ],"primary_terms": {"0": 1},"in_sync_allocations": {"0": ["17d4jyS9RgGEVid4rIANQA"]}}我们可以看到,如果我们没有指定字段类型,就会使用es默认提供的
例如上面的name,默认用了keyword,不可分词
所以我们很有必要在创建时就指定类型
删除索引中指定的数据(根据id)
DELETE hello01/_doc/004{ }修改索引中指定的数据
POST hello02/_update/001{ "doc": { "d2":"Java" } }删除索引中指定的数据
DELETE hello02/_doc/001{ }创建映射字段
PUT /hello05{ "mappings": { "properties": { "name":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }, "say":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" } } }}查看一下hello05索引信息:
{"state": "open","settings": {"index": {"creation_date": "1618410744334","number_of_shards": "1","number_of_replicas": "1","uuid": "isCuH2wTQ8S3Yw2MSspvGA","version": {"created": "7060199"},"provided_name": "hello05"}},"mappings": {"_doc": {"properties": {"name": {"analyzer": "ik_max_word", //说明指定字段类型成功了"type": "text"},"say": {"analyzer": "ik_max_word","type": "text"}}}},"aliases": [ ],"primary_terms": {"0": 1},"in_sync_allocations": {"0": ["lh6O9N8KQNKtLqD3PSU-Fg"]}}指定索引映射字段只能使用一次***
我们再重新往hello05索引添加mapping映射:
PUT /hello05{ "mappings": { "properties": { "name":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }, "say":{ "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word" }, "age":{ "type": "integer" } } }}然后,报错了!!!!!!
{ "error" : { "root_cause" : [ { "type" : "resource_already_exists_exception", "reason" : "index [hello05/isCuH2wTQ8S3Yw2MSspvGA] already exists", "index_uuid" : "isCuH2wTQ8S3Yw2MSspvGA", "index" : "hello05" } ], "type" : "resource_already_exists_exception", "reason" : "index [hello05/isCuH2wTQ8S3Yw2MSspvGA] already exists", "index_uuid" : "isCuH2wTQ8S3Yw2MSspvGA", "index" : "hello05" }, "status" : 400}**注意:==============**
原因是:在我们创建了索引映射属性后,es底层就会给我们创建倒排索引(不可以再次进行修改),但是可以添加新的字段,或者重新创建一个新索引,用reindex把旧索引的信息放到新索引里面去。
所以:我们在创建索引mapping属性的时候要再三考虑
不然,剩下没有指定的字段就只能使用es默认提供的了
使用"_mapping",往索引添加字段
我们上面说过,mapping映射字段不能修改,但是没有说不能添加,添加的方式有一些不同。
PUT hello05/_mapping{ "properties": { "ls":{ "type": "keyword" } } }使用_reindex实现数据迁移
使用场景:当mapping设置完之后发现有几个字段需要“修改”,此时我们可以先创建一个新的索引,然后定义好字段,然后把旧索引的数据全部导入进新索引
POST _reindex{ "source": { "index": "hello05", "type": "_doc" }, "dest": { "index": "hello06" } }#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in reindex requests is deprecated.{ "took" : 36, "timed_out" : false, "total" : 5, "updated" : 0, "created" : 5, "deleted" : 0, "batches" : 1, "version_conflicts" : 0, "noops" : 0, "retries" : { "bulk" : 0, "search" : 0 }, "throttled_millis" : 0, "requests_per_second" : -1.0, "throttled_until_millis" : 0, "failures" : [ ]}获取索引信息
GET hello05{ }获取指定索引中所有的记录(_search)
GET hello05/_search{ "query": { "match_all": {} }}获取索引指定的数据
GET hello05/_doc/1{ }获取指定索引全部数据(match_all:{})
GET hello05/_search{ }和上面的是一样的
GET hello05/_search{ "query": { "match_all": {} } }match查询(只允许单个查询条件)
match查询是可以把查询条件进行分词的。
GET hello05/_search{ "query": { "match": { "name": "李" //查询条件 } }}{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 0.9395274, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "hello05", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 0.9395274, "_source" : { "name" : "李四", "age" : 3 } }, { "_index" : "hello05", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "4", "_score" : 0.79423964, "_source" : { "name" : "李小龙", "age" : 45 } } ] }}如果我们再加多一个查询条件
GET hello05/_search{ "query": { "match": { "name": "李" , "age": 45 } } }就会报错,原因是match只允许一个查询条件,多条件可以用query bool must 来实现
{ "error" : { "root_cause" : [ { "type" : "parsing_exception", "reason" : "[match] query doesn't support multiple fields, found [name] and [age]", "line" : 6, "col" : 18 } ], "type" : "parsing_exception", "reason" : "[match] query doesn't support multiple fields, found [name] and [age]", "line" : 6, "col" : 18 }, "status" : 400}精准查询(term)和模糊查询(match)区别
match:
GET hello05/_search{ "query": { "match": {"name": "李龙" } } } { "took" : 0, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.0519087, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "hello05", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "4", "_score" : 2.0519087, "_source" : { "name" : "李小龙", "age" : 45 } }, { "_index" : "hello05", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 0.9395274, "_source" : { "name" : "李四", "age" : 3 } } ] }}**==================**
term :
GET hello05/_search{ "query": { "term": {"name": "李龙" } } } { "took" : 0, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 0, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : null, "hits" : [ ] }}区别是:
1:match的查询条件是会经过分词器分词的,然后再去和倒排索引去对比(对比term效率较低)
2:term的查询条件是不会分词的,是直接拿去和倒排索引去对比的,效率较高
3:同样term也是只能支持一个查询条件的
multi_match实现类似于百度搜索
match和multi_match的区别在于match只允许传入的数据在一个字段上搜索,而multi_match可以在多个字段中搜索
例如:我们要实现输入李小龙,然后在title字段和content字段中搜索,就要用到multi_match,普通的match不可以
模拟京东搜索商品
PUT /goods{ "mappings": { "properties": { "title":{ "analyzer": "standard", "type" : "text" }, "content":{ "analyzer": "standard", "type": "text" } } } }GET goods/_search{ "query": { //下面输入华为,会进行分词,然后在title和content两个字段中搜索 "multi_match": { "query": "华为", "fields": ["title","content"] } } }{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.1568705, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.1568705, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc", "price" : "3998" } }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 1.0173018, "_source" : { "title" : "华为P40", "content" : "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼", "price" : "4999" } } ] }}短语(精准)搜索(match_phrase)
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "match_phrase": { "content": "华为P40手机" } } } 结果查不到数据,原因是match_phrase是短语搜索,也就是精确搜索
{ "took" : 0, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 0, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : null, "hits" : [ ] }}指定查询显示字段(_source)
elasticsearch默认的显示字段规则类似于MYSQL的select * from xxx ,我们可以自定义成类似于select id,name from xxx
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "multi_match": { "query": "华为", "fields": ["title","content"] } } , "_source" : ["title","content"] //指定只显示title和content }{ "took" : 2, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.1568705, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.1568705, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc" } }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 1.0173018, "_source" : { "title" : "华为P40", "content" : "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼" } } ] }}排序sort
因为前面设计索引mapping失误,price没有进行设置,导致price是text类型,无法进行排序和filter range,所以我们再添加一个字段,od
POST goods/_update/1{ "doc": { "od":1 }}省略2 3 4
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "multi_match": { "query": "华为", "fields": ["title","content"] } } , "sort": [ { "od": { "order": "desc" //asc升序,desc降序 } } ] }分页
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "match_all": {} } , "sort": [ {"od": { "order": "desc"} } ] , "from" : 0 , "size": 2}{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 4, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : null, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "4", "_score" : null, "_source" : { "title" : "IQOONEO5", "content" : "IQOONEO5 高通骁龙870Soc ,", "price" : "2499", "od" : 4 }, "sort" : [ 4 ] }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "3", "_score" : null, "_source" : { "title" : "小米11", "content" : "小米11 高通骁龙888Soc ,1亿像素", "price" : "4500", "od" : 3 }, "sort" : [ 3 ] } ] }}字段高亮(highlight)
可以选择一个或者多个字段高亮,然后被选择的这些字段如果被条件匹配到则会默认加em标签
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "match": {"title": "华为P40" } }, "highlight": { "fields": {"title": {} } } }结果
{ "took" : 6, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.7309713, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 2.7309713, "_source" : { "title" : "华为P40", "content" : "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼", "price" : "4999", "od" : 1 }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "华为P40" ] } }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.5241971, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc", "price" : "3998", "od" : 2 }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "华为Mate30" ] } } ] }}默认是em标签,我们可以更改他的前缀和后缀,利用前端的知识
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "match": {"title": "华为P40" } }, "highlight": { "pre_tags": "", "post_tags": "" , "fields": {"title": {} } } }{ "took" : 3, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.7309713, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 2.7309713, "_source" : { "title" : "华为P40", "content" : "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼", "price" : "4999", "od" : 1 }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "华为P40" ] } }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.5241971, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc", "price" : "3998", "od" : 2 }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "华为Mate30" ] } } ] }}模仿百度搜索高亮
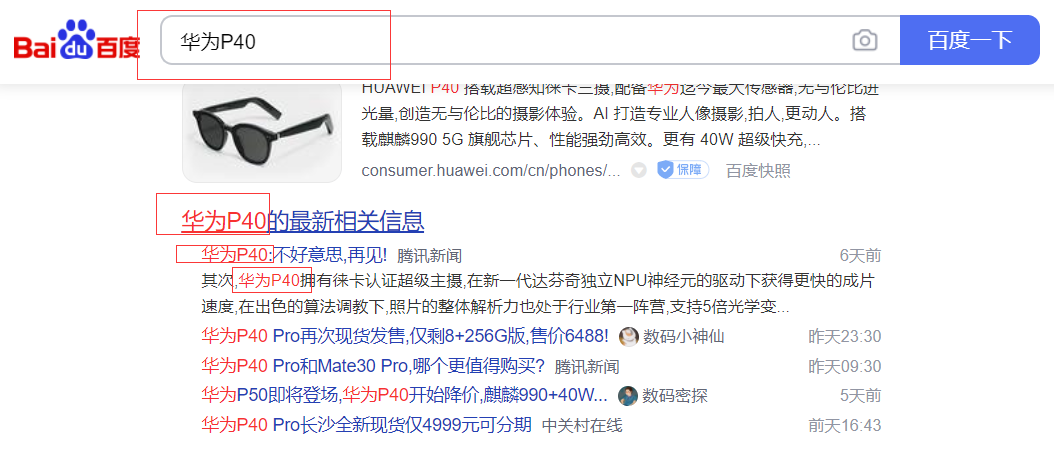
例如百度搜索华为P40,不仅仅是title会高亮,content也会高亮,所以我们可以用multi_match+highlight实现
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "multi_match": { "query": "华为P40", "fields": ["title","content"] } } , "highlight": { "pre_tags": "", "post_tags": "", "fields": { "title": {}, "content": {} } } }{ "took" : 8, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.8157697, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 2.8157697, "_source" : { "title" : "华为P40", "content" : "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼", "price" : "4999", "od" : 1 }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "华为P40" ], "content" : [ "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼" ] } }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.8023796, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc", "price" : "3998", "od" : 2 }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "华为Mate30" ], "content" : [ "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc" ] } } ] }}bool查询(用作于多条件查询)
类似于MYSQL的and or
重点:must 代表and ,should 代表 or
must(and)的使用:
下面我们在must里面给了两个条件,如果这里是must,那就必须两个条件都要满足
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "title": "华为" } }, { "match": {"content": "MATE30" } } ] } }}结果:
{ "took" : 10, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 1, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.9512205, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 2.9512205, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc", "price" : "3998", "od" : 2 } } ] }}should(or)的使用:
should里面同样有两个条件,但是只要满足一个就可以了
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "bool": { "should": [ { "match": { "title": "华为" } }, { "match": {"content": "MATE30" } }] } }}结果:
{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 2, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.9512205, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 2.9512205, "_source" : { "title" : "华为Mate30", "content" : "华为Mate30 8+128G,麒麟990Soc", "price" : "3998", "od" : 2 } }, { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_score" : 1.5241971, "_source" : { "title" : "华为P40", "content" : "华为P40 8+256G,麒麟990Soc,贼牛逼", "price" : "4999", "od" : 1 } } ] }}过滤器,区间条件(filter range)
比如我们要实现,输入title=xx,我们如果想得到price>4000作为一个条件,可以用到这个。
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "title": "小米" } } ],"filter": { "range": { "price": {"gt": 4000 } } } } }}{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 1, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 2.4135482, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "goods", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "3", "_score" : 2.4135482, "_source" : { "title" : "小米11", "content" : "小米11 高通骁龙888Soc ,1亿像素", "price" : "4500", "od" : 3 } } ] }}查看整个es的索引信息
GET _cat/indices?velasticsearch的Java Api
准备阶段
1.导入elasticsearch高级客户端依赖和elasticsearch依赖(注意版本要和本机的es版本一致),我们本机现在用的是7.6.1的es
<dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId> <version>7.6.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch</artifactId> <version>7.6.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.75</version> </dependency>2.打开RestHighLevelClient的构造器:
public RestHighLevelClient(RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder) { this(restClientBuilder, Collections.emptyList()); }我们发现需要传入一个RestClientBuilder,但是这个对象我们需要通过RestClient来得到,而不是RestClientBuilder
3.打开RestClient:
public static RestClientBuilder builder(HttpHost... hosts) { if (hosts == null || hosts.length == 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("hosts must not be null nor empty"); } List nodes = Arrays.stream(hosts).map(Node::new).collect(Collectors.toList()); return new RestClientBuilder(nodes); }我们发现RestClient的builder可以得到RestClientBuilder,然后我们点进去看HttpHost:
public HttpHost(String hostname, int port, String scheme) { //es所在主机名,es的端口号,协议(默认http) this.hostname = (String)Args.containsNoBlanks(hostname, "Host name"); this.lcHostname = hostname.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT); if (scheme != null) { this.schemeName = scheme.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT); } else { this.schemeName = "http"; } this.port = port; this.address = null; }4.然后我们就配置好了如下:
HttpHost httpHost = new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http"); RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder = RestClient.builder(httpHost); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(restClientBuilder); 5.为了方便,我们可以把这个RestHighLevelClient交给SpringIOC容器管理,后面我们自动注入即可
@Configurationpublic class esConfig { @Bean public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){ HttpHost httpHost = new HttpHost("localhost",9200,"http"); RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(httpHost); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); return restHighLevelClient; } }索引操作
java elasticsearch api操作索引都是用restHighLevelClient.indices().xxxxx()的格式
创建索引
//创建索引 @Test public void createIndex() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); //new一个创建索引请求,并传入一个创建的索引名称 CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("java01"); //向es发送创建索引请求。 CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = restHighLevelClient.indices().create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); restHighLevelClient.close(); }删除索引
//删除索引 @Test public void deleteIndex() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); //new一个删除索引请求,并传入需要删除的索引名称 DeleteIndexRequest deleteIndexRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest("java01"); //resthighLevelClient发送删除索引请求 restHighLevelClient.indices().delete(deleteIndexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT); restHighLevelClient.close(); }检查索引是否存在
//检查索引是否存在 @Test public void indexExsit() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); GetIndexRequest getIndexRequest = new GetIndexRequest("goods"); boolean exists = restHighLevelClient.indices().exists(getIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(exists); }文档操作
创建指定id的文档
//创建文档 @Test public void createIndexDoc() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("hello"); //指定文档id indexRequest.id("1"); /** * public IndexRequest source(Map source, XContentType contentType) throws ElasticsearchGenerationException { * try { * XContentBuilder builder = XContentFactory.contentBuilder(contentType); * builder.map(source); * return this.source(builder); * } catch (IOException var4) { * throw new ElasticsearchGenerationException("Failed to generate [" + source + "]", var4); * } * } * source有很多种方法,哪种都可以,我现在选的是Map的方法添加key:value */ Map<String,Object> source=new HashMap<>(); source.put("a_age","50"); source.put("a_address","广州"); //在es里面,一切皆为JSON,我们要把Map用fastjson转换成JSON字符串,XContentType指定为JSON类型 indexRequest.source(JSON.toJSONString(source), XContentType.JSON); IndexResponse response = restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println("response:"+response); System.out.println("status:"+response.status()); }删除指定id的文档
//删除文档 @Test public void deleteDoc() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("hello"); deleteRequest.id("1"); DeleteResponse delete = restHighLevelClient.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(delete.status()); }修改指定id的文档
//修改文档 @Test public void updateDoc() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); /** * 通过下面的方法去调用 * public UpdateRequest(String index, String id) { * super(index); * this.refreshPolicy = RefreshPolicy.NONE; * this.waitForActiveShards = ActiveShardCount.DEFAULT; * this.scriptedUpsert = false; * this.docAsUpsert = false; * this.detectNoop = true; * this.id = id; * } */ UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("hello","1"); Map<String,Object> source=new HashMap<>(); source.put("a_address","河源"); updateRequest.doc(JSON.toJSONString(source),XContentType.JSON); UpdateResponse response = restHighLevelClient.update(updateRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); System.out.println(response.status()); }获取指定id的文档
//获取文档 @Test public void getDoc() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("hello"); getRequest.id("1"); GetResponse response = restHighLevelClient.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); String sourceAsString = response.getSourceAsString(); System.out.println(sourceAsString); }搜索(匹配全文match_all)
//搜索(匹配全文match_all) @Test public void search_matchAll() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); /** * public SearchRequest(String... indices) { * this(indices, new SearchSourceBuilder()); * } */ SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("hello"); //相当于文本 SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); MatchAllQueryBuilder matchAllQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery(); searchSourceBuilder.query(matchAllQueryBuilder); //相当于search的query searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } }搜索(模糊查询match)
//模糊搜索match @Test public void search_match() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(); //查询文本 SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); MatchQueryBuilder matchQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.matchQuery("a_address", "广州"); searchSourceBuilder.query(matchQueryBuilder); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } }搜索(多字段搜索multi_match)
//搜索(多字段搜索multi_match) @Test public void search_term() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("goods"); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("华为","title","content")); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } }搜索(筛选字段fetchSource)
fetchsource方法相当于_source
//fetchsource实现筛选字段(_source) @Test public void search_source() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("goods"); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); searchSourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery()); /** * public SearchSourceBuilder fetchSource(@Nullable String[] includes, @Nullable String[] excludes) { * FetchSourceContext fetchSourceContext = this.fetchSourceContext != null ? this.fetchSourceContext : FetchSourceContext.FETCH_SOURCE; * this.fetchSourceContext = new FetchSourceContext(fetchSourceContext.fetchSource(), includes, excludes); * return this; * } * */ String[] includes={"title"}; //包含 String[] excludes={}; //排除 searchSourceBuilder.fetchSource(includes,excludes); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } }分页、排序、字段高亮
我们要把下面的es命令行代码转换成Java代码
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "match": { "title": "华为" } },"sort": [ { "od": { "order": "desc" } } ] ,"from": 0, "size": 1, "highlight": { "pre_tags": "", "post_tags": "", "fields": { "title": {} } } }Java 实现
//分页,排序,字段高亮 @Test public void page_sort_HighLight() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("goods"); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); MatchQueryBuilder matchQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "华为"); searchSourceBuilder.query(matchQueryBuilder); //分页==== searchSourceBuilder.from(0); searchSourceBuilder.size(1); //======= //排序 searchSourceBuilder.sort("od", SortOrder.DESC); //字段高亮 //=========高亮开始== HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder(); //构建高亮的前缀后缀标签pre_tag和post_tag highlightBuilder.preTags(""); highlightBuilder.postTags(""); //highlightBuilder.field()方法我们用一个String类型的 /** * public HighlightBuilder field(String name) { * return this.field(new HighlightBuilder.Field(name)); * } */ highlightBuilder.field("title"); //如果还需要更多字段高亮,则多写一遍field方法// highlightBuilder.field(); //第二个字段高亮// highlightBuilder.field(); //第三个字段高亮 。。。。。以此类推 searchSourceBuilder.highlighter(highlightBuilder); //====================高亮结束 searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits(); //hits里面封装了命中的所有数据 for (SearchHit hit : hits) { Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields(); System.out.println("highlightMap:"+highlightFields); //通过title这个key去获取fragments //fragment里面是高亮之后的字段内容(很重要,可以用来覆盖原来没高亮的字段内容) 华为Mate30 System.out.println("fragments:"+Arrays.toString(highlightFields.get("title").getFragments())); } restHighLevelClient.close(); }布尔搜索(bool)
实现类似如下es代码:
GET goods/_search{ "query": { "bool": { "should": [ { "term": { "title": { "value": "华" } } }, { "term": { "title": {"value": "米" } } } ] } }}Java实现:
//布尔搜索(bool) @Test public void search_bool() throws IOException { RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")); RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(builder); SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("goods"); SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder(); //通过searchSourceBuilder对象构建bool查询对象 BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery(); //这里should只能写一个,如should里面有多个条件,可以写多个should /** * * "should": [ * { * * "term": { * "title": { *"value": "华" * } * } * * }, * { * * "term": { * "title": { * "value": "米" * } * } */ //例如上面should有两个条件,我们就要写两个should boolQueryBuilder.should(QueryBuilders.termQuery("title","华")); boolQueryBuilder.should(QueryBuilders.termQuery("title","米")); searchSourceBuilder.query(boolQueryBuilder); searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder); SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); SearchHit[] hits = search.getHits().getHits(); for (SearchHit hit : hits) { System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString()); } restHighLevelClient.close(); }es实战(京东商品搜索)
从京东上爬取数据
1:导入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.jsoup</groupId> <artifactId>jsoup</artifactId> <version>1.12.1</version> </dependency>2.创建实体类:
public class goods{ private String img; //商品图片 private String price; //商品价格 private String title; //商品标题 public goods() { } public goods(String img, String price, String title) { this.img = img; this.price = price; this.title = title; } public String getImg() { return img; } public void setImg(String img) { this.img = img; } public String getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(String price) { this.price = price; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } @Override public String toString() { return "goods{" + "img='" + img + '\'' + ", price='" + price + '\'' + ", title='" + title + '\'' + '}'; }}3.利用jsoup解析爬取京东商城搜索(核心),编写工具类:
@Componentpublic class jsoupUtils { private static RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient; @Autowired public void setRestHighLevelClient(RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient) { jsoupUtils.restHighLevelClient = restHighLevelClient; } /** *封装了京东搜索功能,把搜索的数据添加进es中 */ public static void searchData_JD(String keyword) { BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest(); try { URL url = null; try { url = new URL("https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=" + keyword); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Document document = null;//jsoup解析URL try { document = Jsoup.parse(url, 30000); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Element e1 = document.getElementById("J_goodsList"); Elements e_lis = e1.getElementsByTag("li"); for (Element e_li : e_lis) { //这边可能获取到多个价格,因为有些有套餐价格,我们可以获取第一个价格 Elements e_price = e_li.getElementsByClass("p-price"); String text = e_price.get(0).text(); //这里获取的价格可能有多个,正常价和京东PLUS会员专享价,所以我们要进行切分 String realPirce = "¥"; int x = 1; //默认第一个就是¥的符号,也从1开始遍历,如果还有¥符号就break即可 for (int i = 1; i < text.length(); i++) { if (text.charAt(i) == '¥') { break; } else { realPirce += text.charAt(i); } } //商品图片 Elements e_img = e_li.getElementsByClass("p-img"); Elements img = e_img.get(0).getElementsByTag("img"); //因为京东的商品图片不是封装到src里面的,而是封装到懒加载属性==data-lazy-img String src = img.get(0).attr("data-lazy-img"); System.out.println("http:" + src); //价格 System.out.println(realPirce); //商品标题 Elements e_title = e_li.getElementsByClass("p-name"); String title = e_title.get(0).getElementsByTag("em").text(); System.out.println(title); IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("jd_goods"); //添加信息 Map<String,Object> good=new HashMap<>(); good.put("img","http:" + src); good.put("price",realPirce); good.put("title",title); IndexRequest source = indexRequest.source(JSON.toJSONString(good), XContentType.JSON); bulkRequest.add(source); } //批量操作,减少访问es服务器的次数restHighLevelClient.bulk(bulkRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } }}4.使用工具类:
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); jsoupUtils.searchData_JD("vivo"); }有了数据我们就可以用来展示到页面上了。。。。。


